Introduction
Enterprises are accelerating their adoption of IoT in order to support the growing demands of remote operations & monitoring, digital transformation initiatives, improvements in network infrastructure landscape and the rollout of commercial 5G, especially 5G Standalone / 5G Advanced.
Significant spending is expected on IoT projects – IDC predicts that worldwide IoT spending will exceed US $1 trillion by 2026, growing from approximately $805.7 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4% between 2023 and 2027.
Enterprises looking to expand the reach of their IoT solutions across multiple geographic regions often experience similar if not identical roadblocks:
- Delayed Deployments: Enterprises have to manage multi-operator contracts in parallel with regulatory approvals which often lead to protracted delays in the launch of services.
- Regulatory fragmentation: Compliance with multi-geography data privacy regulations and policies while improving the customer journey and experience overall.
- Roaming complexity: Roaming contract negotiations and settlement, reconciliations across multiple billing formats since devices often have to stay connected across boundaries and borders
- Billing diversity: Taxes, tariffs, and usage models vary widely, making cost management difficult.
- Operational silos & Inefficiency: As a stop-gap measure enterprises often run separate region-specific systems, leading to higher support costs, reduced ROI and poor visibility of operations.
- Compliance Risks: Not meeting the compliance requirements of localized breakout, data routing and lack of integration interfaces to support demand of lawful interception can result in fines or forced network topology redesigns.
- Revenue Leakage: Not able to plug connectivity gaps across regions and geographies stall enterprise IoT rollout and makes them lose their competitive advantage.
The IoT connectivity management platform (CMP) plays a pivotal role to overcome these barriers and it serves as the central enabler. Operated by the MVNE, the CMP unifies multiple operator networks into a single, unified environment, offering capabilities such as SIM lifecycle management, e-SIM provisioning, roaming enablement, billing consolidation and regulatory compliance assurance.
MVNOs by leveraging the native capabilities of the CMP, configure, customize and deliver enterprise-ready connectivity services aligned to specific business needs.
This gives them the ability to orchestrate connectivity at scale — managing SIM activation and provisioning, configuring APN profiles for seamless global access, and applying enterprise‑specific roaming and policy rules.
Together the MVNE-MVNO collaboration delivers a solution which enables enterprises to scale IoT connectivity globally.
MVNE Role – Technical Backbone
What the MVNE Brings to the table
1. Pre‑Integrated Connectivity Backbone
- Core Network Integrations with MNOs: MVNEs bring to the table a deep core integration with the network elements such as the HLR/HSS, PCRF, OCS, AAA, Packet gateways, DIAMETER/SIP signalling gateways across multiple operator domains.
2. Satellite & Non‑Terrestrial Connectivity Options
- There are significant changes being worked on in the network domain to include IoT beyond terrestrial operator offerings; MVNEs increasingly support 3GPP‑standardized Non‑Terrestrial Networks (NTN). With Release 17, NB‑IoT and LTE/4G technologies have been extended into satellite domains, enabling direct‑to‑device IoT connectivity via LEO/MEO/GEO constellations without requiring proprietary hardware.
- Building on this, Release 19 introduces advanced 5G NTN capabilities. These enhancements also pave the way for standalone satellite IoT services, where devices can connect directly to satellite networks independently of terrestrial coverage.
- By embedding NTN gateways, roaming agreements, and compliance reporting into the CMP, MVNEs allow enterprises to provision dual‑mode SIMs and eSIMs that seamlessly switch between terrestrial and satellite coverage, enforce unified policy rules across both domains, and normalize satellite usage records into consolidated billing and compliance frameworks.
- This ensures IoT deployments remain connected, standards‑compliant, and regulator‑ready across maritime, aviation, remote industrial, and disaster‑recovery scenarios where terrestrial networks are unavailable.
3. Unified Connectivity Management Platform
- A Unified CMP with out of the box (OOTB) capabilities enables MVNOs to consolidate IoT operations such as Authentication, SIM-lifecycle management, provisioning, activation, device management, monitoring, billing, and reporting across the diverse networks.
4. Global Reach with Roaming Enablement
- Pre-configured roaming agreements, existing integrations in place with GRX/IPX hubs and multiple clearing houses MVNEs ensure seamless roaming.
5. Billing and Settlement Normalization
- Single unified view of the collected and aggregated usage records(CDRs) from multiple MNOs
- Standardizes fragmented tariffs to enterprise friendly bundles, taxes, and billing formats to ensure consistent and transparent charging across multiple network operators
- Exposes flexible APIs that allow MVNOs to implement enterprise-specific billing models and streamlines settlement process.
6. Regulatory & Compliance Assurance
- Out of the box capabilities for regulatory recommended standardized interfaces to support lawful interceptions across multiple jurisdictions
- Enables localized data breakout and routing to comply with country-specific data and privacy regulations
- Provides comprehensive audit trails and compliance reporting to support different regulatory frameworks such as GDPR.
7. Security & Trust
- Role-based access controls, data encryption, and detailed audit logs ensure that the connectivity management platform is secure by design.
End to End MVNE-MVNO Framework Architecture
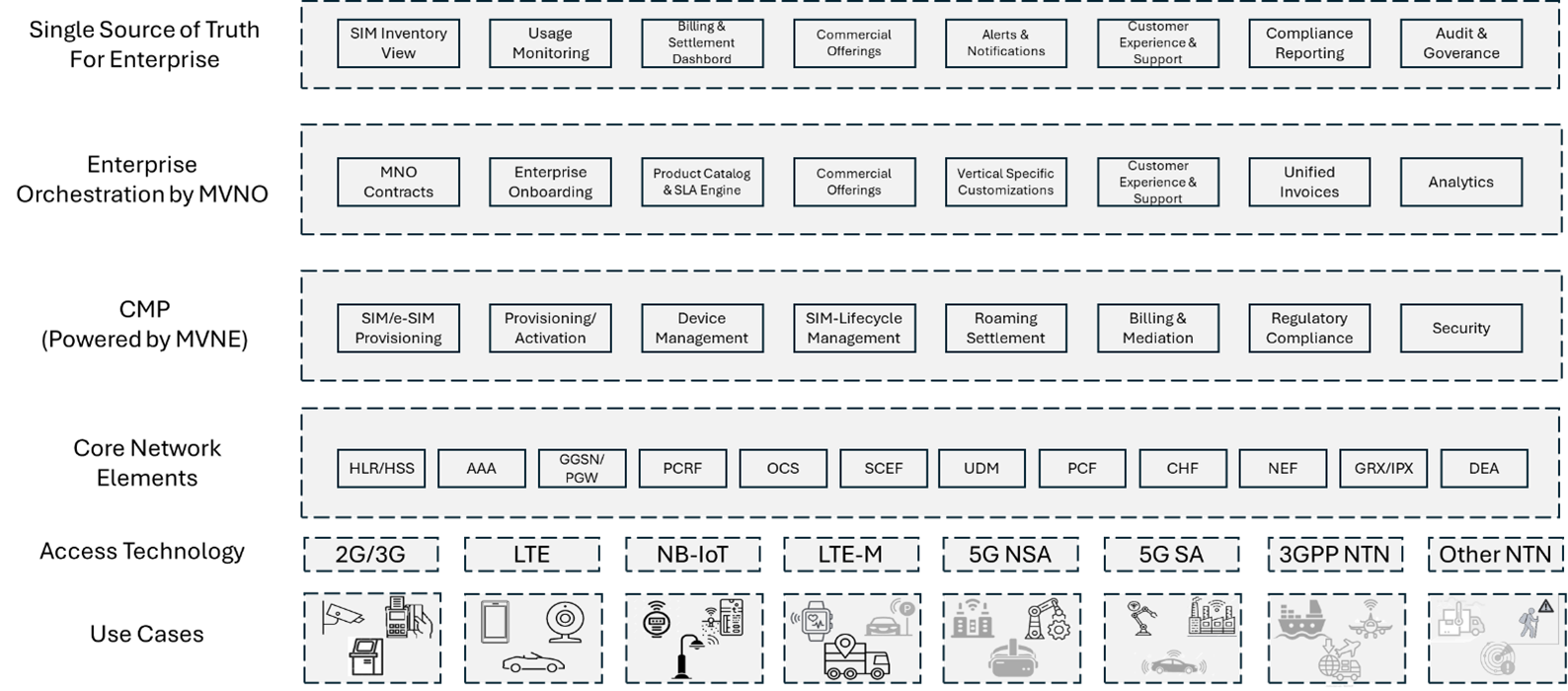
MVNO Role – Enterprise Orchestration
What the MVNO Brings to the table
1. Enterprise Contracting & Commercial Interface
- MVNOs act as the single commercial interface for enterprises, owning contracts and delivering tailored connectivity packages.
- By leveraging the MVNE’s CMP technical capabilities, MVNOs tailor the products and services into market-ready offerings, including flexible pricing models, defined SLAs, and vertical-specific bundles aligned to enterprise requirements.
2. Customization & Value-Added Services
- MVNOs can differentiate themselves by creating industry-specific solutions and rules, such as healthcare-ready compliance features for consent collection, pooled data plans for the fleet of logistics trackers with device level tracking, or smart city deployments with bundled connectivity and IoT management dashboards. All these can be value-adds on top of the MVNE platform.
3. Customer Experience & Support
- MVNOs manage the full enterprise relationship, handling everything from onboarding, service activation, daily service assurance activities and ongoing support.
- Using MVNE dashboards and APIs, they give enterprises clear, real-time visibility into their services, along with proactive alerts, and SLA monitoring.
4. Operational Simplification
- Using the MVNE’s consolidated billing and reporting capabilities, MVNOs deliver transparent, unified invoices and compliance-ready reports to enterprises.
- This significantly reduces operational overhead for enterprises and strengthens long-term trust.
5. Expansion Flexibility
- MVNOs help enterprises expand their IoT deployments across regions without the burden of managing multiple operator contracts.
- Global roll outs are supported with local regulatory compliance, using the MVNE’s pre-integrated roaming, data sovereignty, and regulatory capabilities.
6. Innovation & Differentiation
- MVNOs can innovate faster by focusing on tailoring the CMP to vertical specific solution needs such as customer onboarding flows and alignment of workflows as per enterprise business needs, while the MVNE manages the complexity of multi-operator integration, security, and compliance.
Value For Enterprise
- Reduced Integration Overhead: Pre-integrated MVNE network capabilities eliminate operator-specific builds, enabling faster onboarding, lower deployment costs, and quicker time-to-market.
- Unified Operational Visibility: A single CMP provides centralized control of SIM lifecycle, monitoring, and billing across networks, improving operational oversight and reducing support effort.
- Seamless Global Scalability: Pre-negotiated roaming and existing operator agreements allow enterprises to expand IoT deployments across regions without contract or integration delays.
- Compliance Ready: Built-in lawful interception, local breakout, and audit trails ensure deployments are regulator-ready from day one, reducing compliance risk.
- Financial Clarity: Automated billing and settlement across multiple operators remove cost opaqueness and unexpected charges.
- Future-Proof for Innovation: A modular, platform-driven architecture supports seamless expansion across new IoT verticals and geographies. Enterprises can extend their services into smart cities, healthcare, automotive, or industrial IoT use cases without re-engineering connectivity, ensuring long-term scalability and adaptability.
Conclusion
The MVNE–MVNO partnership delivers more than connectivity it creates enterprise outcomes that matter: risk reduction, financial predictability, speed to market, operational resilience, scalability, and differentiated customer experiences. This makes it the most scalable and future‑proof model for global IoT connectivity.

Guest Blogs are written by carefully selected Experts. If you also want to create a Guest blog then Contact us.
