Introduction Different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs
The telecommunications industry is evolving at an unprecedented rate, with dozens of Mobile Brands / MVNOs emerging every year. To help you understand the various different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs, we thought it might be useful to provide a small explanation.
We will go over the following:
- What is a Mobile Network Operator (MNO)?
- What is a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO)?
- How do MNOs differ from MVNOs?
- What are the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs?
- Is there a hard split between thin/light MVNOs and thick/full MVNOs?
- How do Branded Resellers, Light MVNOs, and Full MVNOs differ?
- Overall summary of the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs
What is a Mobile Network Operator (MNO)?
A Mobile Network Operator (MNO) is a communications provider that has direct access to licensed frequency spectrum like 3G, 4G, 5G, 6G. It also owns and operates its own Radio Access Network (RAN).
In addition, MNOs manage their own core network infrastructure. This includes Operations Support Systems (OSS), Business Support Systems (BSS), and other tools necessary for running mobile / cellular businesses.
More succinctly, MNOs own all the components necessary to sell and deliver mobile services like voice, text / SMS, international calling, etc. As such, they typically have complete control over their data plans, applications, services, rating and billing processes, customer care practices, and marketing and sales strategies.
Some of the most common MNOs include AT&T, América Móvil, Vodafone, Bharti Airtel Limited, MTN, Telefonica, T-Mobile, Orange, Telefonica, etc.
Mobile Network Operators can also expand their services with a range of communication services to customers. Such as telephone, internet, and television. These services are typically provided over a network of infrastructure, including telephone lines, fiber optic cables, and satellite systems.
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO)?
To understand what different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs there are you must first understand what an MVNO is. A Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) is a company that provides wireless communications services. the MVNO has neither direct access to licensed frequency spectrum nor their own radio antennas. Moreover, most MVNOs do not typically own their own (full) core network infrastructure.
Instead, MVNOs facilitate mobile connectivity for their subscribers by purchasing bulk access to network services from MNOs. And from other network service providers at wholesale rates or from an MVNA. As such, MVNOs can set retail prices independently, in alignment with the needs of their intended market segments.
What is the difference between an MNOs and MVNOs?
The critical difference is that MNOs own their own wireless network infrastructure (including antennas) and MVNOs do not. To facilitate mobile services to their subscribers:
- MVNOs must purchase access to radio network infrastructure either directly from MNOs,
- or indirectly from Mobile Virtual Network Aggregators (MVNA) or Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNE).
It should also be noted that MVNOs are increasingly popular among consumers since they offer more flexibility than MNOs. Indeed, because MNOs tend to have much larger customer bases, their services need to appeal to broader swathes of the market. This leads to generic services, rigid pricing, one-size-fits-all data plans, and uninspiring branding.
In contrast, the pricing and branding independence enjoyed by MVNOs enables them to home in on ultra-specific customer segments. Like low-income consumers, students, the older age group — basically anyone that does not fall neatly into the generic plans offered by MNOs.
Along the same lines, MVNOs enable businesses to diversify or enhance existing offerings. For example, many Internet Service Providers (ISP) have begun offering mobile services alongside ADSL. This is to retain current customers, attract new customers, and bolster revenue.
Now that you know the difference between MNO and MVNO, we will explain the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs.
What are the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs?
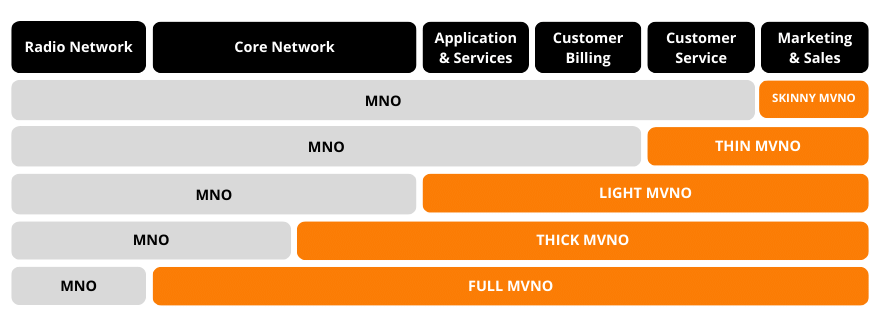
There are five Different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs, the type determines roughly the features, and flexibility you will get. There is NOT a hard line between the different types but broadly speaking, there are five MVNO types. Whereas the Light MVNO and Full MVNO are most used. See also MVNE, MVNA and MVNO differences explained in a simple way:
1. What is a Branded Reseller (Skinny) MVNO?
Of the five different types of MVNOs, Branded Resellers (Skinny MVNOs) are the most lightweight, making them the easiest to set up, with the lowest barriers to entry. Branded Reseller are also sometimes referred to as “no-frills MVNOs” because they typically offer a limited range of services and features. Indeed, Branded Resellers are MVNOs that leverage predefined settings, tariffs, and bundles from existing service providers (MNOs and/or MVNEs or even other MVNOs) and sell them under their own brands. Since they defer to these readymade environments, they can focus on things that are more in line with their expertise — things like sales, marketing, relationship-building, etc. Typically there is NO license needed for a Branded Reseller (Skinny MVNO).
Two of the most well-known Branded Resellers are Walmart Family Mobile and ALDI mobile, both of which leverage their brand recognition to sell mobile services to their robust customer bases. Branded reseller MVNOs also tend to have the shortest time-to-market and lowest startup costs. This means they’re one of the most convenient options for businesses that want to grow their brand, diversify their offerings, or expand into industries like telecommunications or the Internet of Things (IoT).
2. What is a Thin MVNO?
Just like Branded Resellers, Thin MVNOs (Service Providers) delegate operational management of core network services to host operators (MNOs and/or MVNEs or even other MVNOs). Thin MVNOs acquire a lot from the host network such Core Network, Radio Access, and most of the time the management of applications, billing and Rating. Typically there is NO license needed for a Thin MVNO.
However, Thin MVNOs tend to have a bit more flexibility in defining their services, bundles, tariffs, and plans. Next to the Sales and Marketing they normally also have their own Customer Service.
3. What is a Light MVNO?
Just like Branded Resellers and Thin MVNOs, Light MVNOs (Enhanced Service Providers) delegate operational management of Core Network services to host operators (MNOs and/or MVNEs). Light MVNOs are also sometimes referred to as “mid-tier MVNOs” because they offer a good balance of flexibility and cost-effectiveness. In some countries a license or a Light MVNO might be required.
However, Light MVNOs have substantially more flexibility in defining their services, bundles, tariffs, and plans then Skinny or Thin MVNOs. While Light MVNOs acquire Core Network and Radio Access from host networks, they keep everything else in-house. The Light MVNO has its own Business Support System (BSS) and its own Operational Support System (OSS). Which include the management of applications and services, rating and billing, customer care, and sales and marketing.
4. What is a Thick MVNO?
The thick MVNO is basically an expansion of the Light MVNO setup. The thick MVNO will have some Core Network elements of their own which will broaden the flexibility and give the MVNO some additional options. For the radio access, they negotiate service agreements (also known as wholesale agreements) with MNOs, MVNAs. In most countries a license or a thick MVNO is required.
Why would you go for a thick MVNO? For example, expanding the light/thin MVNO with a GGSN/PWG will give you more control over the date usage of the subscribers. Therefore you can offer additional options like free data usage to a certain service during a certain time.
5. What is a Full MVNO?
Finally, Full MVNOs are the most sophisticated option. As a Full MVNO, you will typically have complete control over everything except radio access, which remains in the purview of MNOs. Full MVNOs are also sometimes referred to as “premium MVNOs” because they offer the most flexibility and control.
This means you have your own Core Network elements — like Home Location Register (HLR), Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN), SMS Center (SMSC), Packet Data Network Gateway (PWG), Session Border Controller (SBC), etc. For the radio access, they negotiate service agreements (also known as wholesale agreements) with MNOs, MVNAs. In most countries a license or a Full MVNO is required.
Generally, Full MVNOs set up and maintain their own core network elements and infrastructure and manage their own SIM cards (or eSIMs), call flows, SMS flows, and data flows. As such, Full MVNOs have complete control over all network services and offerings. Whereas Light MVNOs are ideal for service- and brand-oriented businesses, the Full MVNO model is better-suited for larger telecommunications projects.
Is there a hard split between thin/light MVNOs and thick/full MVNOs?
There is no hard split between thin/light and thick/full MVNOs. The primary distinction between the two is that thin/light MVNOs do not own any core network elements whereas thick/full MVNOs own at least one core network element.
That said, which core network elements are owned by a thick/full MVNO depends entirely on which core network elements are provided by their host network. For example, let’s assume that a certain MNO allows for the use of their packet data gateways but not their subscriber registry. Any thick/full MVNO that uses their network can implement their packet data gateways but will need to come up with their own subscriber registry.
How do Branded Resellers, Light MVNOs, and Full MVNOs differ?

Full MVNOs are the most flexible of the types of MVNOs, meaning they have the most freedom when it comes to developing, bundling, pricing, and branding their offerings. This is because they own and manage more aspects of running a mobile service than do other types of MVNOs. Branded Resellers, on the other hand, are the least flexible since they only get to control things like sales and marketing.
Simply put, the more aspects an MVNO wants to manage, the more they will need to invest and the more flexibility they’ll have. Of course the setup time increase as well. Therefore, for businesses and entrepreneurs looking to launch their own mobile services, it’s important to consider these trade-offs when coming up with business cases, marketing plans, and organizational strategies.
Overall summary different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs
There are many different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs, each with its own set of characteristics and capabilities. As stated the most common types of MVNOs are Branded Resellers, Thin MVNOs, Light MVNOs, Thick MVNOs, and Full MVNOs.
Branded Resellers are the most lightweight, with the lowest barriers to entry. They typically offer a limited range of services and features, and they rely on a host network to provide their infrastructure. Thin MVNOs have more flexibility than Branded Resellers, and they typically own some services like Customer Care. Light MVNOs have the most flexibility of all without owning any of the Core Network Elements. Thick MVNOs are a hybrid of Light and Full MVNOs, and they own some core network elements and rely for the others on a host network for others. Full MVNOs are the most sophisticated type of MVNO, and they own their own Core Network and all the infrastructure that is necessary to run a mobile service.
The type of MVNO that is best for a business will depend on its specific needs and requirements. Businesses that are looking for a quick and easy way to get into the mobile business should consider Branded Resellers. Businesses that need more flexibility and control should consider Thin, Light, Thick, or Full MVNOs. Businesses that need to support a large number of customers should consider Full MVNOs.
Various other terms for the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs
Terms such as Airtime Reseller, Basic MVNO, Digital virtual network operators (DVNOs), Enhanced Service Provider (ESP), Connectivity Service Provider (CSP), Extended MVNO, Reseller MVNO, Service Provider MVNO, Hybrid MVNO, Cloud MVNO, DATA MVNO, IN MVNO, Medium MVNO, On-brand MVNO, Enhanced MVNO, Sub-brand MVNO, VNO, MVO. The solution providers/vendors use these terms to differentiate themselves from others. Of course this does not make it easier for you. Therefore, for you it would be best for you to use the globally used terms.
Table with the key characteristics of the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs
Branded Reseller (Skinny MVNO)
Most lightweight, lowest barriers to entry, limited range of services, relies on host network for everything
Thin MVNO
More flexibility than Branded Resellers, has its own Customer Care
Light MVNO
Most flexibility of all, without owning any of the core network components
Thick MVNO
Hybrid of Light and Full MVNOs, owns some core network elements and relies on host network for others
Full MVNO
Most sophisticated type of MVNO, owns own core network and all infrastructure.
There is more then the different types of Mobile Brands / MVNOs?
You have also Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNEs) and Mobile Virtual Network Aggregators (MVNAs). This you need to know as well, since they are your potential Solution providers / Vendors. For more information see also MVNE, MVNA and MVNO differences explained in a simple way.