Core Network Architecture for MVNOs: A Simplified Breakdown for Business Teams
Why Business Teams Should Care
The MVNO core network isn’t just a technical backend—it’s the engine that powers customer experience, monetization, and strategic agility. Whether you’re launching a new brand, expanding into Spain, or pitching investors, understanding your core architecture helps you:
- Control service quality (latency, call clarity, data speed)
- Design flexible pricing models (tiered plans, bundles, real-time charging)
- Enable partnerships (IoT, fintech, content platforms)
- Scale across markets (modular architecture = faster expansion)
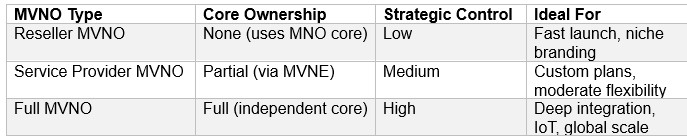
Core Components—Simplified for Business Teams
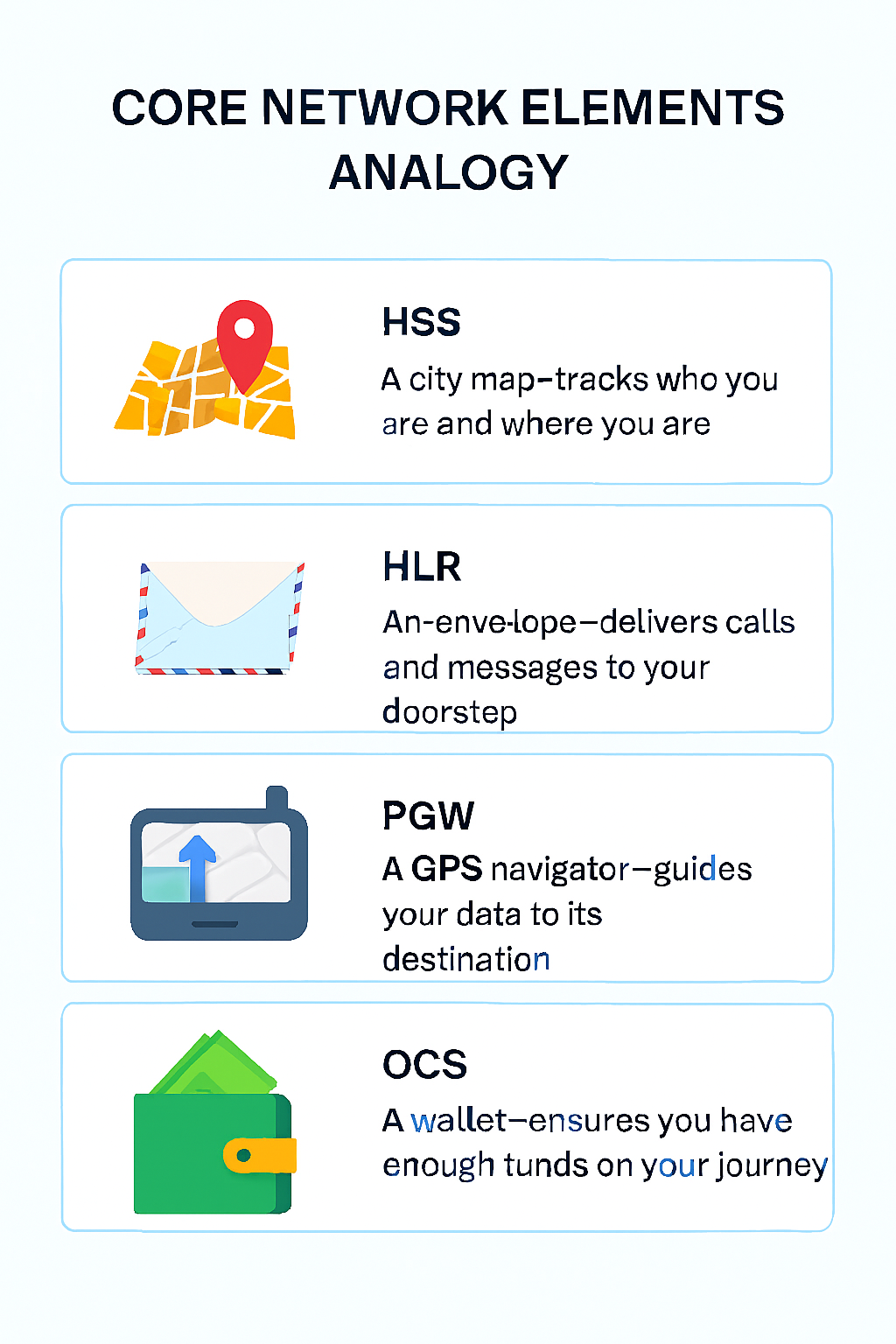
1. HLR / HSS (Subscriber Management)
Think of this as your customer database— these systems store and manage subscriber profiles, including SIM authentication, roaming permissions, and service entitlements.
Strategic Insight: For MVNOs, controlling this layer means owning the customer identity lifecycle—critical for enabling roaming, multi-SIM offerings, and personalized service tiers.
2. GMSC / PGW / GGSN (Gateways)
These route voice and data traffic—like telecom routers connecting users to the internet. These gateways route voice and data traffic between the MVNO’s core and external networks, including the internet and PSTN.
Strategic Insight: Optimizing gateway performance directly impacts latency, call quality, and data throughput—making them essential for delivering premium user experiences and meeting SLAs.
3. SMSC / MMSC (Messaging Centers)
Deliver SMS and MMS—critical for alerts, engagement, and two-factor authentication.
These centers handle the delivery and routing of SMS and MMS messages, including alerts, marketing campaigns, and authentication codes.
Strategic Insight: Messaging reliability is key for customer engagement, especially in fintech, e-commerce, and onboarding flows where timely delivery builds trust and drives conversions.
4. OCS / PCRF (Charging & Policy Control)
OCS enables real-time charging and balance management, while PCRF enforces service policies like data caps, speed throttling, or content access.
Strategic Insight: Together, these components allow MVNOs to create dynamic pricing models, launch targeted promotions, and offer differentiated service tiers—all crucial for ARPU growth. You can launch promotions that respond to customer behavior instantly and tailor service access—e.g., throttling data after limits, enabling parental controls, or offering premium speed tiers.
5. CDR (Call Detail Records)
Tracks usage—essential for billing, analytics, and compliance.
CDRs log every transaction—calls, messages, data sessions—with timestamps, duration, and usage metrics.
Strategic Insight: Beyond billing, CDRs fuel analytics, churn prediction, and regulatory compliance. Structuring them for business intelligence unlocks insights into customer behavior and network performance. They’re the foundation of your analytics strategy.
Here’s a business-friendly breakdown of the key elements:
Imagine your business with a dedicated team assigned to each core network element—experts owning subscriber management, gateways, messaging, charging, and analytics. Suddenly, SIM provisioning becomes a strategic lever, not a support ticket. Your PGW team fine-tunes data flows for premium users in real time. Messaging specialists launch hyper-personalized campaigns with near-zero latency. Charging architects roll out dynamic pricing by region, and your CDR analysts surface churn signals before they become revenue leaks. This isn’t just operational excellence—it’s a blueprint for loyalty, agility, and scalable growth.
The Future: AI, Modularity & Customer-Centric Redesign
With the rise of AI, cloud-native infrastructure, and modular telecom stacks, MVNOs are no longer bound by rigid legacy designs. Core elements like the PGW (Packet Gateway)—once static and hardware-bound—are being reimagined to prioritize customer experience over network constraints.
- AI-driven traffic shaping allows for personalized data speeds and latency optimization.
- Dynamic PGW configurations can prioritize premium users, throttle congestion, or enable content-specific routing.
- Cloud-native cores make it possible to scale, test, and iterate without downtime.
This evolution isn’t theoretical—it’s happening. MVNOs that embrace flexible, customer-first architecture are already seeing gains in loyalty, retention, and revenue growth.
Enablement Checklist
Before launching or scaling, business teams should ask:
- What parts of the core do we own vs lease?
- Can we support real-time charging and flexible policies?
- How easily can we integrate with external platforms (CRM, billing, analytics)?
- What’s our fallback plan if a core component fails?
- Are our CDRs structured for business intelligence—not just billing?
- Are we exploring AI or modular redesigns to improve customer satisfaction?
Final Thought: Architecture as a Growth Lever
In my young and growing experience enabling MVNOs across Africa and Europe, on a small scale, the most successful teams treat architecture not as a cost center—but as a strategic asset. When business leaders understand the core, they unlock new revenue models, better customer experiences, and faster market entry.
Whether you’re onboarding developers, pitching investors, or expanding into other geographies—your architecture is your growth story. Own it.

Guest Blogs are written by carefully selected Experts. If you also want to create a Guest blog then Contact us.
